Joint European Research Infrastructure of Coastal Observatories: Science, Service, Sustainability
JERICO-S3 facilitates the integration of marine sensing technology into research data infrastructures to better observe the coastal ecosystem.
The Joint European Research Infrastructure for Coastal Observatories (JERICO-RI) is a system of systems strengthening the European network of coastal observatories. It provides a powerful and structured European Research Infrastructure (RI) dedicated to observing and monitoring the complex marine coastal seas. JERICO-RI aims to
- provide services for the delivery of high-quality environmental data
- enable access to solutions and facilities as services for researchers and users
- create product prototypes for EU marine core services and users
- support excellence in marine coastal research to better answer societal and policy needs
JERICO-S3 provides a state-of-the-art, fit-for-purpose and visionary observational RI, as well as expertise and high quality data on European coastal and shelf seas. It significantly enhances the current value and relevance of the JERICO-RI by implementing the science and innovation strategy elaborated in successive JERICO projects since 2010.
JERICO-S3 targeted a more integrated scientific approach to better observe the coastal ecosystem. This in turn elevated the scientific excellence of the regional and local ecosystems. The project implemented major user-driven improvements in terms of observing the complexity of coastal seas and continuous monitoring of biology, access to facilities, data and services, best practices and performance indicators, as well as innovative monitoring strategies. These also covered cooperation with other European RIs (EuroARGO, EMSO, DANUBIUS, ICOS, EMBRC) and international scientific communities, industry and other stakeholders, as well as strategy alignment with COPERNICUS/CMEMS, EMODNET and GEO/GEOSS.
52°North focused on technological innovation activities. Our team worked on the advancement of Sensor Web components, such as the Helgoland Sensor Web Viewer and data access services based on the OGC SWE standards. Our aim was to improve the usability of interoperable data exchange workflows and concepts for marine sensor data.
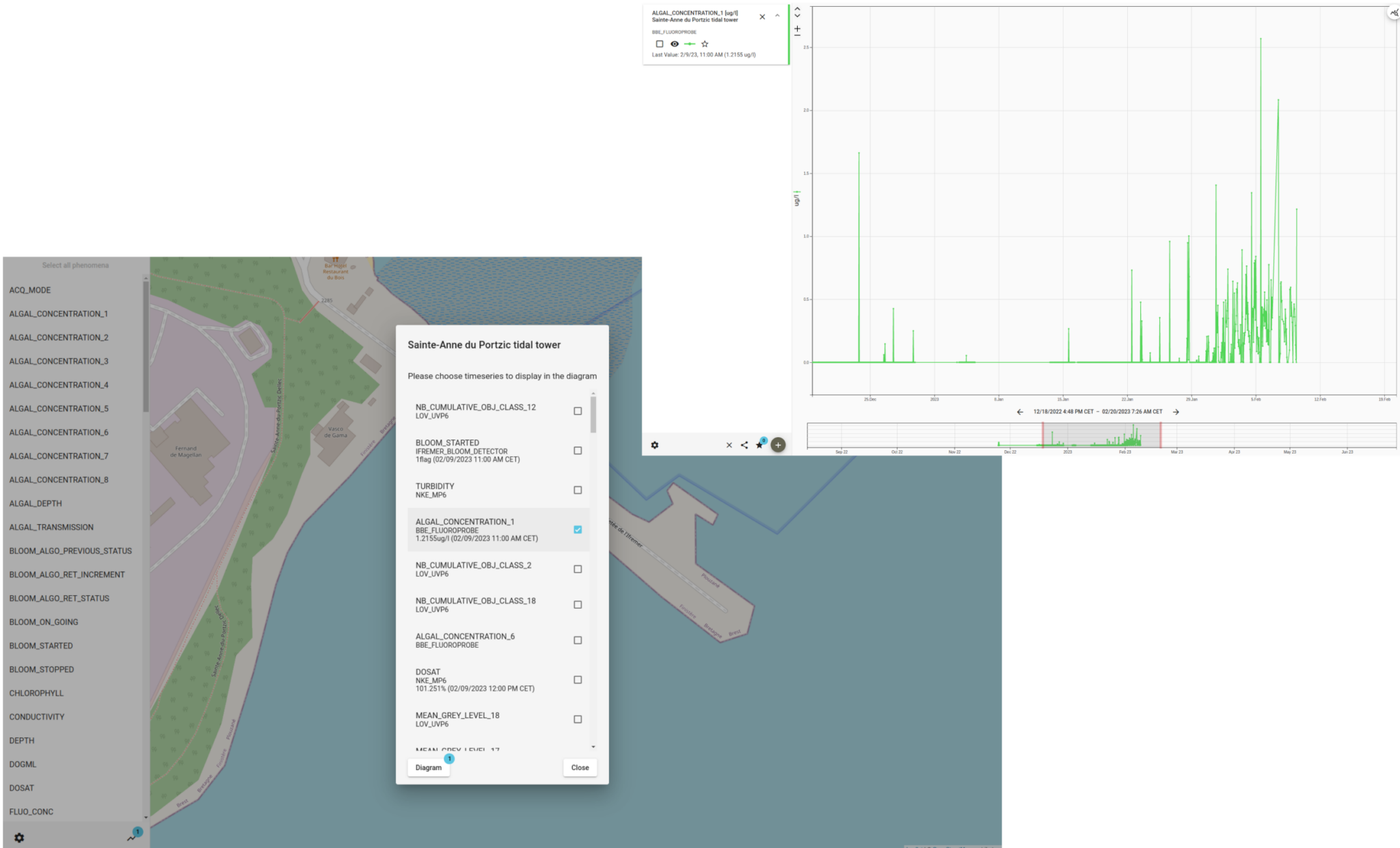
52°North supported the consortium in a pre-demo test activity deploying an autonomous underwater coastal observatory (coastal EMSO Generic Instrument Module, cEGIM) in 8 m water depth in the Sainte Anne du Portzic Bay, near IFREMER (Brest, France). The objective of the activity was to test the entire cEGIM platform, including automated sensor configuration changes, data acquisition, storage, and communication. 52°North provided an OGC SensorThings API and a Helgoland instance for data storage and visualization. In 2024, 52°North contributed to deliverables with documentation and insights from the test activities to conclude the project.
Partners
39 partners, including:
Coordinator, Institut français de recherche pour l’exploitation de la mer (Ifremer), France
Alfred-Wegener-Institut, Helmholtz-Zentrum für Polar- und Meeresforschung (AWI), Germany
Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR), Italy
ETT S.p.A., Italy
European Global Ocean Observing System (EuroGOOS), Belgium
Helmholtz-Zentrum Geesthacht Zentrum für Material- und Küstenforschung GmbH (HZG), Germany
Istituto Nazionale di Oceanografia e di Geofisica Sperimentale (OGC), Italy
Plataforma Oceánica de Canarias (PLOCAN), Spain

