Scenario-based Multi-risk Assessment in the Andes Region
Using the RIESGOS architecture, local municipalities and stakeholders can easily identify the impact of potential disaster situations and plan accordingly.
RIESGOS 2.0 is the direct successor to the successful RIESGOS project, which addressed challenges of increased risks to society caused by natural hazards, such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes or tsunamis with a focus on the Andes region in South America. It aimed to effect more efficient risk management based on more reliable information. In particular, the project addressed complex interactions, such as cascading effects of certain hazards and risks, as well as many of the underlying sources of uncertainty.
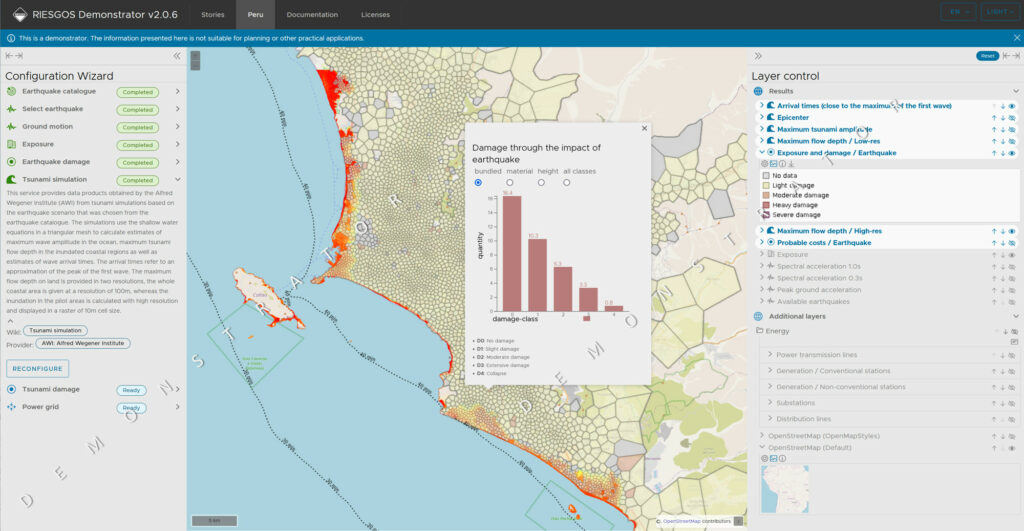
RIESGOS 2.0 developed novel scientific approaches related to the assessment of different hazards and risks. This included the analysis of dynamic exposure, vulnerability and the modelling of cascading effects and possible failures. Modular Web services integrated into a flexible and scalable multi-risk information system demonstrator provided the foundation of the RIESGOS 2.0 software architecture. End-users from civil protection and disaster management authorities received a tool to simulate and analyze complex multi-risk scenarios.
52°North was responsible for the conceptual design and implementation of an interoperable architecture for a multi-risk analysis and information system for the Andes region. Our tasks comprised:
- the analysis of requirements
- the design of a message-driven processing architecture that improves the overall flow data and information products
- the implementation of selected web services as instances of the OGC API Processes
- the conceptual design of integrating uncertainty and quality information into the data products of the distributed web services
- a contribution to market analysis and development of exploitation perspectives (focus on the publication as open source software).
In 2024, 52°North focused on finalizing the project work within the di erent focus areas. Our team prepared a final online workshop involving stakeholders from the South American partner countries. We successfully showcased the “RIESGOS Demonstrator” and all 51 participants discussed several interesting follow-up topics. The project team bid farewell to six successful years of the RIESGOS and RIESGOS 2.0 projects.
Partners
Coordinator: Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR), Germany
Helmholtz-Zentrum Potsdam Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum (GFZ), Germany
Alfred-Wegener-Institut (AWI), Germany
Technische Universität München (TUM), Germany
geomer GmbH, Germany
Sachverständigenbüro für Luftbildauswertung und Umweltfragen, Germany
DIALOGIK, Germany
