Co-designed Citizen Observatories Services for the EOS Cloud
Developing interoperable components to support Citizen Science projects via the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC)
Cos4Cloud (Co-designed citizen observatories for the EOS Cloud) designed, prototyped and implemented services that address the Open Science challenges shared by citizen observatories active in the fields of biodiversity and environmental quality monitoring. To support citizen observatories, project work focused on the development of services that help improve the data and information quality. Technologies used to implement these services included deep machine learning, automatic video recognition, advanced mobile app interfaces, and other cutting-edge technologies based on data models and data protocols validated by traditional science. The new services provide mechanisms to ensure the visibility and recognition of data contributors and tools to improve networking between various stakeholders. Novel innovative digital services were developed by integrating Citizen Science products generated by different providers. The consortium implemented the services according to open standards to ensure their interoperability. The European Open Science (EOS) Cloud hub provided an agile, fit-for-purpose and sustainable site, including a discovery service, to both traditional and citizen scientists.
Stakeholders in society, government, industry, academia, agencies, and research drove a user-oriented design of the new services by co-designing the service requirements. Cos4Cloud integrated Citizen Science in the European Open Science Cloud, bringing Citizen Science projects as a service to the scientific community and society at large.
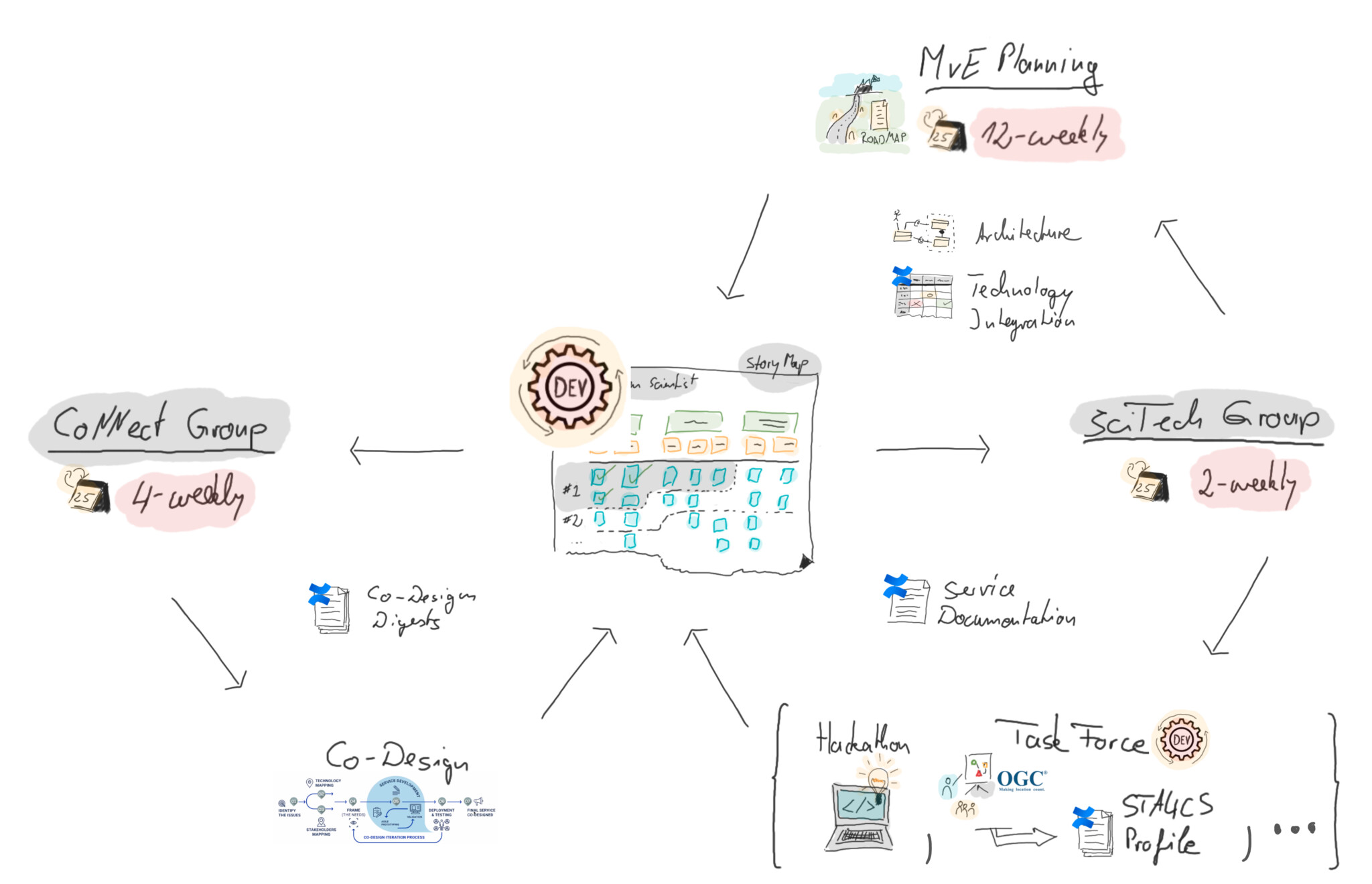
52°North contributed to the definition of the architecture and the development of interoperability standards, profiles and best practices. We led the project work to define a set of agile methodologies and documentation instructions. Our other contributions included interoperability, conformance and performance testing, and technology readiness assessment. Additionally, we supported networking, dissemination, and international standardization activities.
In 2022, our team finalized the fit-for-purpose agile methodology that respects the individual differences of all partners. It provides the framework for team-level technical development and overall integration of project-level activities (e.g., co-design process) throughout the project lifecycle. In addition, we created an agile testing plan to ensure that the features developed and the integration of citizen observatories and services developed serve the project’s overall goal.
Our software engineers also helped develop the service architecture, focusing on interoperability. We contributed to the STAPlus extension for the SensorThings API (v1.1).
The extension leverages data modeling and workflows in citizen observatories. It covers not only aspects focused on citizen science, but also, for example, observation ownership, licensing, and their relationships, and can be applied to other domains as well. With partners SecureDimensions and CREAF, we submitted the OGC Best Practice for using SensorThings API with Citizen Science. The OGC community has approved the Best Practice document for publication.
Project Partners
Coordinator: Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC), Spain
Conservation Education & Research Trust, United Kingdom
Centro de Investigacion Ecologica y Aplicaciones Forestales, Spain
Institut national de recherche eninformatique et automatique (INRIA), France
DYNAIKON LTD, United Kingdom
Bineo Consulting S.L., Spain
Norbert Carl Schmidt, The Netherlands
The Open University, United Kingdom
Secure Dimensions GmbH, Germany
Sveriges lantbruksuniversitet (SLB), Sweden
Ethniko kai Kapodistriako Panepistimio Athinon, Greece
Verein der Europäischen Bürgerwissenschaften e.V. (ECSA), Germany
Trébola Organización Ecológica, Colombia
Science for Change S.L., Spain
